AI 系列:Vector Databases
2023-11-18
Work in Progress
This chapter is still being written & reviewed. Please do post links & discussion in the comments below, or open a pull request!
Some ideas:
-
PGVector
-
short sections for each of the rows from the table below
矢量数据库 Vector databases 在过去一年因生成式人工智能的兴起而受到广泛关注,但矢量嵌入(vector embedding)的概念已存在多年。
- 在进行图像分类时,神经网络提取的“特征”就是“矢量嵌入”。
- 这些矢量嵌入,包含了有关图像的精炼(“压缩”)信息。
- 对于基于文本的模型,矢量嵌入捕获了
单词之间的关系,使模型能够理解语言。 - 嵌入(
Embeddings)可以存储在数据库中以供日后查找和检索使用。
Table 11 Comparison of Vector Databases#
| Vector Database | Open Source | Sharding | Supported Distance Metrics | Supported Indices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| weaviate/weaviate | 🟢 Yes | 🟢 Yes | cosine, dot, L2 squared, hamming, manhattan | HNSW, HNSW-PQ |
| qdrant/qdrant | 🟢 Yes | 🟢 Yes | cosine, dot, euclidean | HNSW |
| milvus-io/milvus | 🟢 Yes | 🟢 Yes | cosine, dot, euclidean, jaccard, hamming | HNSW, FLAT, IVF-FLAT, IVF-PQ |
| RedisVentures/redisvl | 🟢 Yes | 🟢 Yes | cosine, inner product, L2 | HNSW, FLAT |
| chroma-core/chroma | 🟢 Yes | 🔴 No | cosine, inner product, L2 | HNSW |
| Pinecone | 🔴 No | 🟢 Yes | cosine, dot, euclidean | HNSW, FLAT, LSH, PQ |
LLM Embeddings#
大型语言模型(LLM)是在大规模文本语料库(例如维基百科)上进行训练的。当模型处理这些文本时,它根据单词在上下文中的用法,对单词做了标识。
- 高维向量:随着模型从数据中学习,它将每个
单词表示为一个高维向量,通常具有数百或数千个维度。向量中的值编码,代表了单词的含义。 - 近似语义:在对大量文本进行训练后,具有
相似含义的单词在向量空间中更加接近。 - 泛化能力:产生的单词向量,体现出了单词之间的语义关系,使得模型在语言任务中具有更好的泛化能力。这些预训练的嵌入,被用在初始化像BERT这样的大型语言模型的第一层。
总之,通过在大量文本数据上训练模型,最终得到了一个专门设计来捕捉单词之间关系的模型,即向量嵌入(vector embeddings)。
大型语言模型就像一位语言专家,通过阅读大量文章,学会了如何理解单词。
当模型读文章时,它会观察单词在文章中的用法,并根据它们在上下文中的关系给每个单词打上标签。
这就好像将每个单词都放在一个特殊的盒子里,这个盒子里有很多信息,包括这个单词的意思以及它和其他单词之间的联系。
这样,模型学到的这些标签(或盒子)可以帮助它更好地理解语言,并在需要时做出更智能的回答。
Turning text into embeddings#
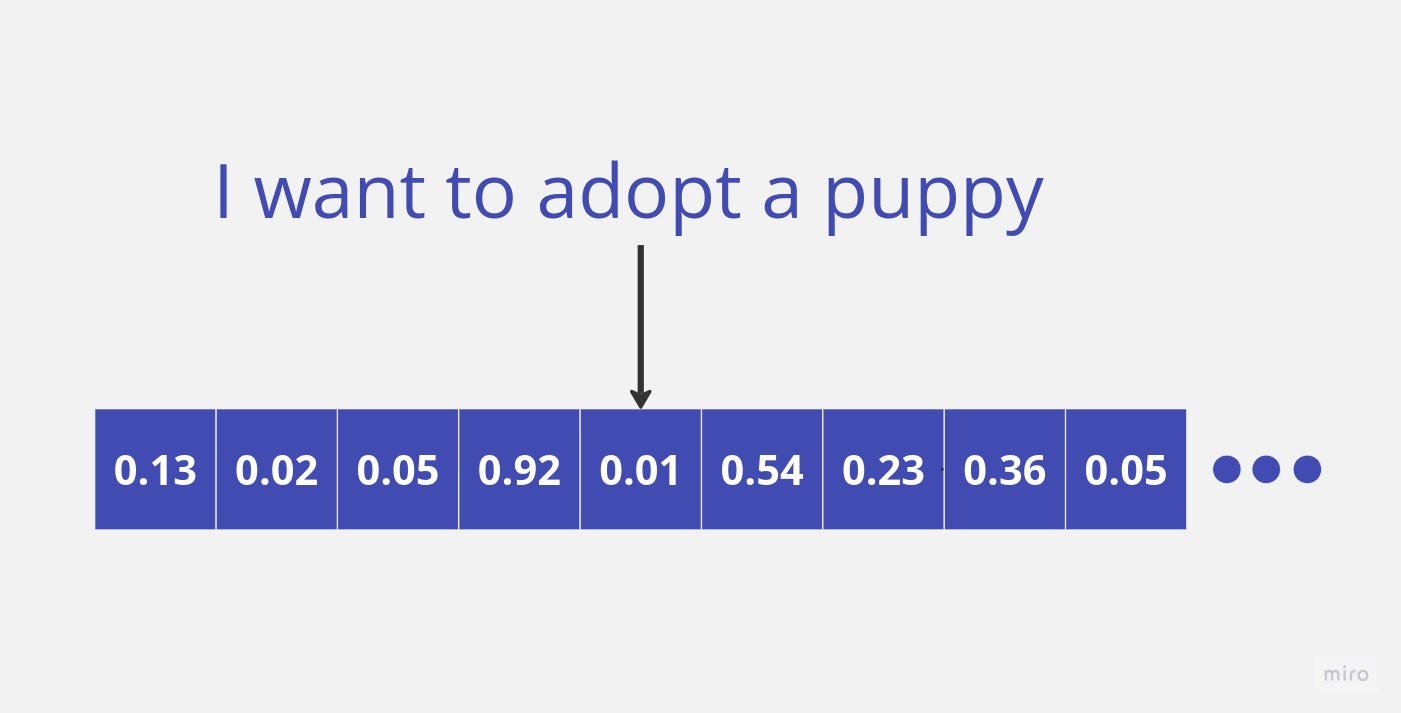
Fig. 62 Vector Embeddings#
Let’s take the sentence from the image above as an example: “I want to adopt a puppy”
-
Each word in the sentence is mapped to its corresponding vector representation using the pre-trained word embeddings. For example, the word “adopt” may map to a 300-dimensional vector, “puppy” to another 300-dim vector, and so on.
-
The sequence of word vectors is then passed through the neural network architecture of the language model.
-
As the word vectors pass through the model, they interact with each other and get transformed by mathematical functions. This allows the model to interpret the meaning of the full sequence.
-
The output of the model is a new vector that represents the embedding for the full input sentence. This sentence embedding encodes the semantic meaning of the entire sequence of words.
Many closed-source models like text-embedding-ada-002 from OpenAI and the embeddings model from Cohere allow developers to convert raw text into vector embeddings. It’s important to note that the models used to generate vector embeddings are NOT the same models used for text generation.
生成
词向量的模型与用于文本生成的模型并不相同。
- 词向量模型:旨在学习词语的语义关系和上下文表示
- 文本生成模型:是用来根据学习到的信息,生成文本。
这两种模型的目的和功能是不同的。
Embeddings vs Text Generation
-
For NLP, embeddings are trained on a language modeling objective. This means they are trained to predict surrounding words/context, not to generate text.
-
Embedding models are encoder-only models without decoders. They output an embedding, not generated text.
-
Generation models like GPT-2/3 have a decoder component trained explicitly for text generation.
Vector Databases#
矢量数据库Vector databases,可以高效存储和搜索 矢量嵌入(vector embeddings)。
Calculating distance between vectors#
大多数矢量数据库,支持三种主要的距离度量:
- 欧氏距离 Euclidean distance:向量空间中,两点之间的直线距离
- 余弦相似度 Cosine similarity:两个向量之间夹角的
余弦值- 余弦值越大,向量越接近 - 点积 Dot product:
余弦相似度和向量长度(大小)的乘积 - 点积越大,向量越接近
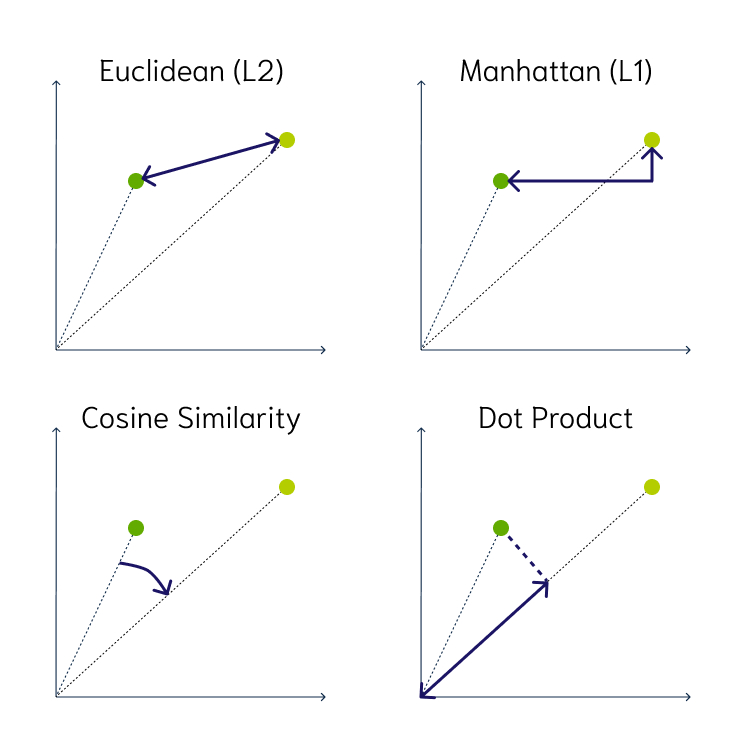
Fig. 63 Vector Distance Metrics#
Vector Indexing#
Even though vector databases can contain metadata in the form of JSON objects, the primary type of data is vectors. Unlike relational databases or NoSQL databases, vector databases optimise operations to make reading and writing vectors as fast as possible.
With vector databases, there are two different concepts of indexing and search algorithms, both of which contribute to the overall performance. In many situations, choosing a vector index involves a trade-off between accuracy (precision/recall) and speed/throughput [148]. There are two primary factors that help organise an index:
-
The underlying data structure,底层的数据结构
-
Level of compression,压缩率
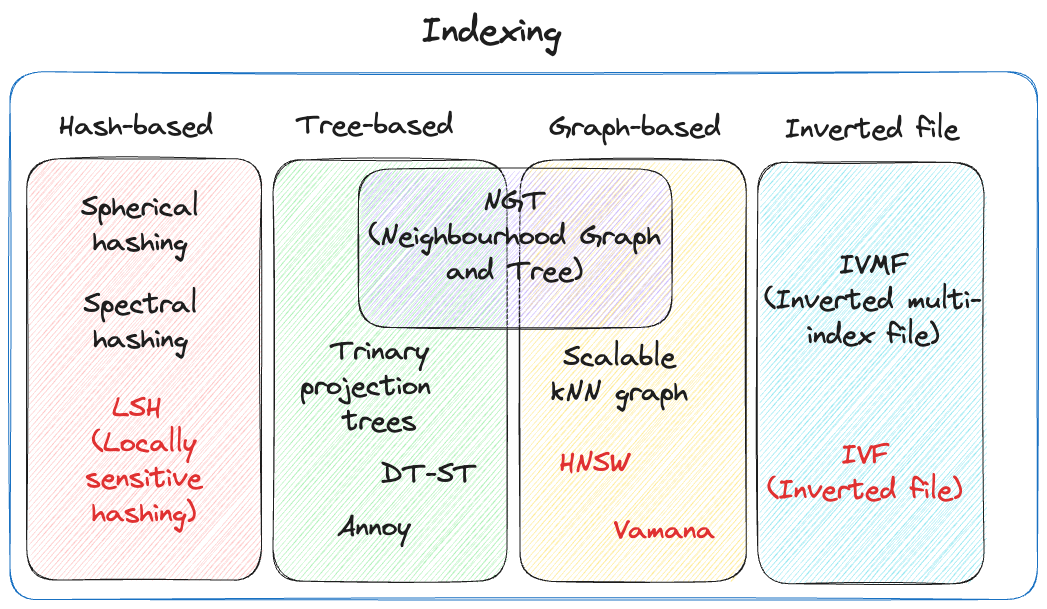
Fig. 64 Vector Indexing#
Hash-based Indexing#
局部敏感哈希(Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH))使用哈希函数,将相似的向量分桶到哈希表中。查询向量也使用相同的哈希函数进行哈希处理,并与已经存在于表中的其他向量进行比较。
这种方法比在整个数据集上进行详尽搜索要快得多,因为每个哈希表中的向量比整个向量空间中的向量要少。虽然这种技术非常快速,但缺点是它的准确性不够。LSH是一种近似方法,因此,更好的哈希函数会产生更好的近似结果,但结果不会是确切的答案。
Tree-based Indexing#
基于树的索引,使用诸如二叉树之类的数据结构,进行快速搜索。树以一种方式创建,使相似的向量分组在同一子树中。spotify/annoy(Approximate Nearest Neighbour Oh Yeah)使用二叉树森林来执行近似最近邻搜索。
- Annoy 在高维数据中表现良好,其中进行精确的最近邻搜索可能会很昂贵。
- 使用这种方法的缺点是
建立索引可能需要大量时间。 - 每当收到新的数据点时,索引无法即时重组,必须从头开始重建整个索引。
Graph-based Indexing#
与基于树的索引类似,基于图的索引通过连接相似的数据点来进行分组。当尝试在高维空间中搜索向量时,基于图的索引非常有用。HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World)(Hierarchical Navigable Small World)是一种流行的基于图的索引,旨在在搜索速度和准确性之间提供平衡。
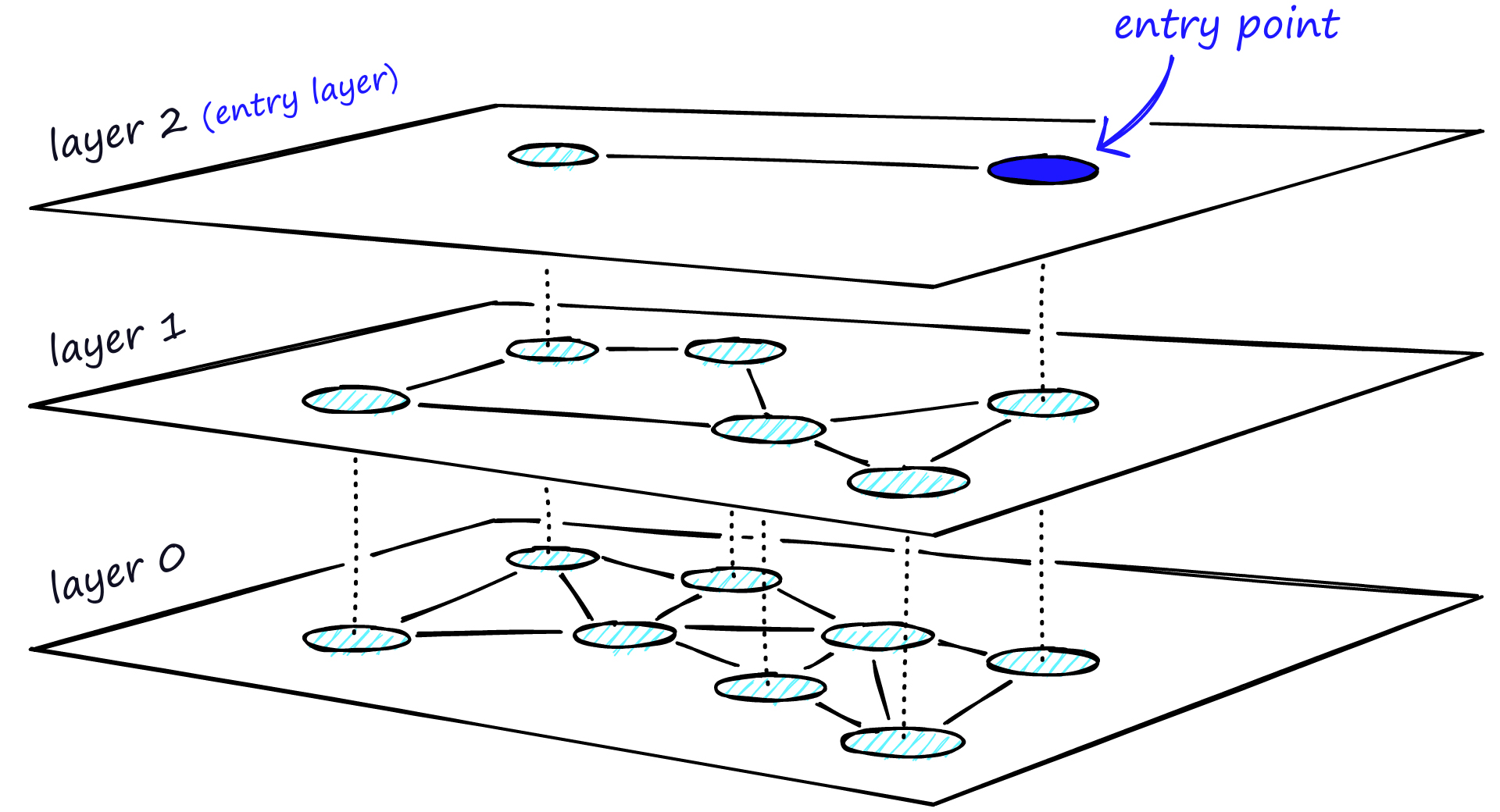
HNSW创建了一个分层图,顶层包含最少的点,底层包含最多的点 [149]。
- 当输入查询进入时,通过最近邻算法搜索顶层。
- 图会逐层向下遍历。
- 在每一层,最近邻算法被运行以找到与输入查询最接近的点。
- 一旦到达底层,将返回与输入查询最近的点。
基于图的索引非常高效,因为它允许在每一层缩小搜索范围从而在高维空间中搜索。然而,重新索引可能具有挑战性,因为可能需要重新创建整个图[149]。
Inverted File Index#
IVF(Inverted File Index)通过将数据集进行分区并为每个分区创建一个中心点(随机点)来缩小搜索空间。
- 这些
中心点,通过K-Means算法进行更新。 - 一旦索引被填充,
最近邻算法会找到离输入查询最近的中心点,然后只在该分区中进行搜索。
虽然IVF在创建索引后,搜索相似点时非常高效,但创建分区和中心点的过程可能会相当慢。
Vector Compression#
Vectors can take up a lot of memory in terms of storage. High dimensional data adds to this problem which can end up making vector search slow and difficult to manage. To tackle this issue, compression is used to reduce the overall footprint of the vector while still retaining the core structure of the data.
向量压缩,但不损失信息量.
There are two kinds of compression techniques:
-
Flat
-
Product Quantisation (PQ)
Flat compression does not modify the vectors and keeps the original structure. When an input query comes in a kNN search is done to find the exact match between the input vector and the vectors present in the vector database. This leads to a high level of accuracy, but it comes at the cost of speed. The search time increases linearly as the size of the dataset grows. When dealing with larger datasets, flat will likely yield poor results in terms of latency.
On the other hand, product quantisation reduces the memory footprint of the original vectors by decreasing the number of dimensions. It splits the original vector into chunks and gives each chunk an id. These chunks are created in a way that the distance between them can be calculated efficiently.
Product Quantisation works well for large datasets and high-dimension spaces. It can greatly speed up the nearest neighbour search and reduce the overall memory footprint by ~97%. The downside of using this compression technique is that it can lead to lower accuracy and recall [150].
有两种压缩技术:
1.平坦压缩(Flat)
平坦压缩不修改向量并保持原始结构。
- 当输入查询时,进行
K近邻搜索(KNN)以找到输入向量与向量数据库中向量的精确匹配位置。 - 这提供了高水平的准确性,但以速度为代价。
- 随着数据集大小的增长,搜索时间会线性增加。当处理较大数据集时,平坦压缩可能导致延迟性能较差。
2.乘积量化(Product Quantisation,PQ)
- 乘积量化通过
减少维度来减小原始向量的内存占用。 - 它将原始向量
分割成块,并为每个块分配一个ID。 - 创建块的方式,可以有效计算
它们之间的距离。 - 乘积量化,适用于
大型数据集和高维空间。 - 它可以极大地加速最近邻搜索,并将整体内存占用降低约97%。
- 使用这种压缩技术,缺点是可能会导致较
低的准确性和召回率。
Searching Algorithms#
Vector indexing is more about selecting the underlying data structure to store the vectors. Vector searching is about picking the algorithm used to search on that data structure.
A basic algorithm used for vector search is kNN (K-Nearest Neighbors). kNN works by calculating the distance between the input vector and all of the other vectors inside the vector database. This algorithm does not scale well as the number of vectors increases, because as the number of vectors increases so does the search time.
There is a more efficient search algorithm commonly used by vector databases called ANN(Approximate Nearest Neighbors). ANN works by pre-computing the distance between the vectors and storing them in a way so that similar vectors are placed closer to each other.
By grouping or clustering similar vectors, the algorithm can quickly narrow down the search space without wandering further away from the input query.
Popular Use-Cases#
A common use case for vector databases is search. Whether it’s searching for similar text or images, this tool can efficiently find the data you are looking for.

Fig. 66 LLM prompt injection with vector databases#
在LLM(大型语言模型)的背景下,向量数据库经常用于从用户的查询中检索信息,以在LLM的提示中使用。向量数据库可以作为LLM的长期记忆,因此只有与输入查询相关的部分,被注入到提示中。
另一个用例是推荐引擎。推荐的本质是寻找相似的产品。在这种情况下,关系型或NoSQL数据库效果不佳,因为不需要精确匹配。向量数据库已被用于各种推荐,从电影到电子商务产品。
Limitations#
While there are many advantages to using vector databases in certain applications, there are also a few issues to be aware of:
-
Data structure
-
Vector databases are optimised to work with only vector data. The underlying data structures may not be suitable for working with tabular or JSON data.
-
For this reason, vector databases should not be used as a replacement for other types of databases as they lack many of the features such as being ACID-compliant.
-
-
Debugging difficulty
-
To humans a vector looks like a random list of numbers. These numbers don’t make any sense to us, so it becomes difficult to interpret what this vector represents.
-
Unlike a relational database where we can read the data in each column, we cannot simply read the vector. This makes vector data difficult to debug, as we have to rely on algorithms and metrics to make sense of the data.
-
-
Indexing issues
-
The way a vector database is indexed is crucial to its search performance.
-
However, due to the way some indices are designed it can be quite challenging to modify or delete data. For some indices, the entire underlying data structure needs to be re-formatted when data changes are made.
-
Future#
-
Vector databases provide a unique solution to problems that are not sufficiently addressed by relational or NoSQL databases
-
Instead of competing directly against prior databases, it has carved out its own category in the tech stack
-
Advancements in indexing and searching algorithms will make vector databases faster and cheaper
-
80–90% of the data daily generated on the internet is unstructured [151]. Most of it is in the form of text, images, and video. Vector databases can help extract value from unstructured data, whether is improving LLM accuracy, image similarity, or product recommendations.
在可预见的未来,向量数据库将会持续存在。它们似乎不太可能取代传统数据库或被其所取代,因为它们各自具有不同的用途。这项技术最终将成为人工智能技术栈中的主流组成部分。
原文地址:https://ningg.top/ai-series-prem-09-vector-db/